Understanding attribution models is essential for modern marketing because they help identify which marketing channels contribute to conversions. By knowing which touchpoints play a role in a customer’s journey, you can make smarter decisions about where to invest your budget. Accurate attribution helps marketers optimize campaigns, improve ROI, and allocate resources more effectively.

What Are Attribution Models?
Attribution models are methods used to assign credit to different marketing channels that influence a customer’s decision to convert. They help track how customers interact with various touchpoints like emails, social media, and ads during their buying journey. Assigning credit to the right channels helps marketers understand which efforts are driving results and where to focus their budget.
Common Types of Attribution Models:
1. First-Touch Attribution Model:
What is First-Touch Attribution?
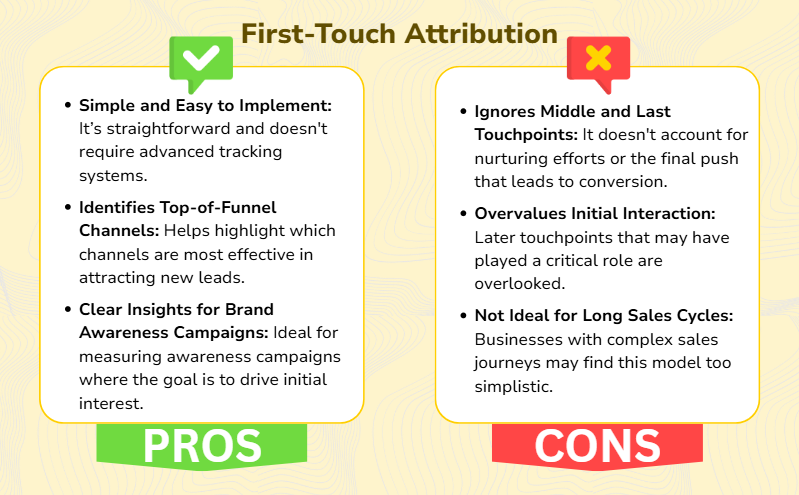
First-touch attribution is a marketing measurement model that assigns 100% of the credit for a conversion or sale to the first interaction a customer has with your brand. This means if a customer first engages with your business through a social media ad and later makes a purchase, the social media ad gets full credit for driving that sale.
How does It work?
- Initial Interaction: The first touchpoint (such as an ad, email, or organic search) is recorded when a potential customer engages with your brand.
- Lead Journey: The customer continues interacting with various channels like emails, websites, or sales calls.
- Conversion: Once the customer makes a purchase or completes a desired action, the first interaction is attributed to the entire conversion value.
When to Use First-Touch Attribution:
- Brand Awareness Campaigns: When the goal is to understand which channels generate the most interest.
- Short Sales Cycles: For businesses with quick decision-making processes.
- Limited Data and Resources: When you need a simple, cost-effective way to measure performance.
2. Last-Touch Attribution Model:
What is Last-Touch Attribution?
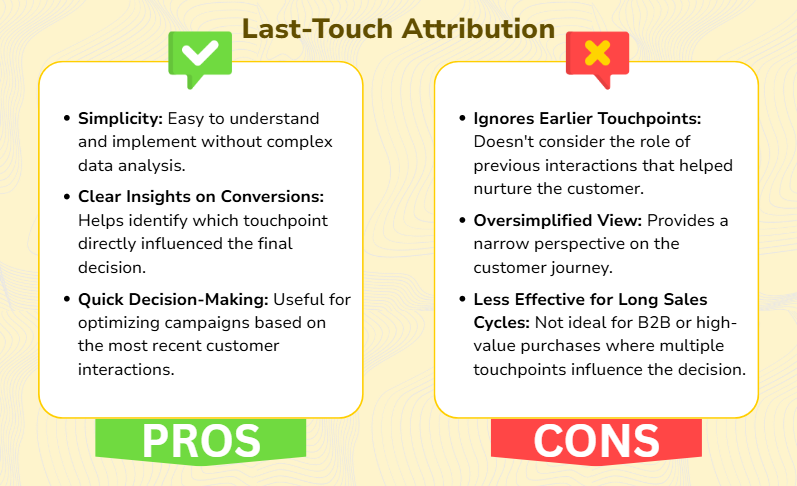
Last-touch attribution is a marketing measurement model that gives 100% credit to the final interaction a customer had before making a purchase or completing a desired action. This means the last marketing channel or touchpoint like an email, paid ad, or social media post is considered the primary reason for the conversion.
For example, suppose a customer first sees a product through a social media ad, reads a blog about it, and finally clicks a promotional email to make the purchase. In that case, the email will receive full credit in a last-touch attribution model.
When to use Last-Touch Attribution:
- E-Commerce Transactions: Where customers make quick purchase decisions.
- Short Sales Cycles: Products or services with minimal customer research involved.
- Campaign Performance Testing: Measuring the direct impact of promotions or limited-time offers.
3. Linear Attribution Model:
What is Linear Attribution?
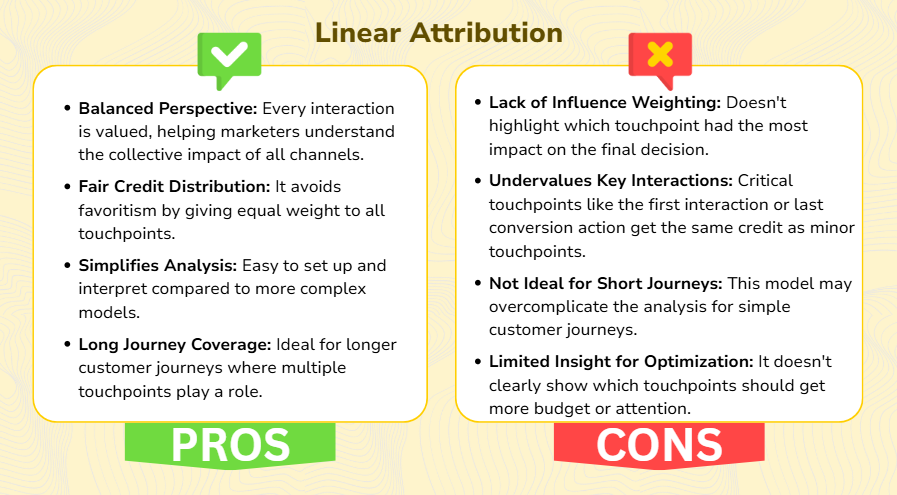
Linear attribution is a marketing attribution model that distributes credit equally across all touchpoints in a customer journey. Whether it’s an email campaign, social media ad, website visit, or demo request, each interaction gets the same percentage of credit for the final conversion. It is ideal for businesses looking for a balanced view of how different marketing efforts work together to drive conversions.
For example, if a customer engages with four marketing touchpoints before making a purchase, each touchpoint receives 25% of the credit.
When to Use Linear Attribution:
This model works best:
- When you have long customer journeys with multiple touchpoints.
- For brand awareness campaigns where every interaction plays a consistent role.
- When your goal is to measure the overall contribution of each channel rather than identifying the single most influential touchpoint.
4. Time-Decay Attribution Model:
What is Time-Decay Attribution?
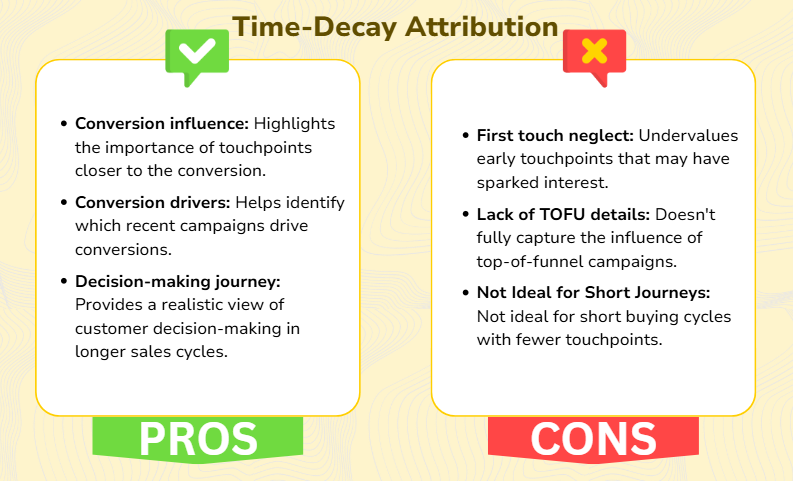
Time-decay attribution is a marketing model that assigns more credit to touchpoints closer to the final conversion. Earlier interactions still receive credit, but the most recent interactions get a higher share. The idea is that the closer a touchpoint is to the conversion, the more influence it likely has on the customer’s decision. It helps you understand how nurturing campaigns and final touchpoints impact conversion decisions.
For example, suppose a customer interacts with five marketing campaigns before making a purchase. In that case, the last interaction might receive 40% of the credit, the one before it 30%, and so on — with earlier touchpoints receiving smaller portions.
When to Use Time-Decay Attribution:
This model is most effective when:
- You have long sales cycles with multiple interactions.
- Later-stage campaigns (like demos or follow-up emails) are key to closing deals.
- You’re focused on optimizing campaigns that drive final conversions rather than brand awareness.
5. Position-Based (U-Shaped) Attribution Model:
What is Position-Based Attribution?
Position-based or the U-shaped attribution model, gives more credit to the first and last touchpoints in a customer journey. Typically, 40% of the credit goes to the first touchpoint (which creates awareness), 40% to the last touchpoint (which drives the conversion), and the remaining 20% is split evenly among any middle interactions. It helps businesses understand which channels are best at capturing interest and which ones drive final conversions.
For example, if a customer clicks on a social media ad, downloads a whitepaper, and later responds to an email before making a purchase, the social media ad and email would each get 40% of the credit, while the whitepaper gets 20%.
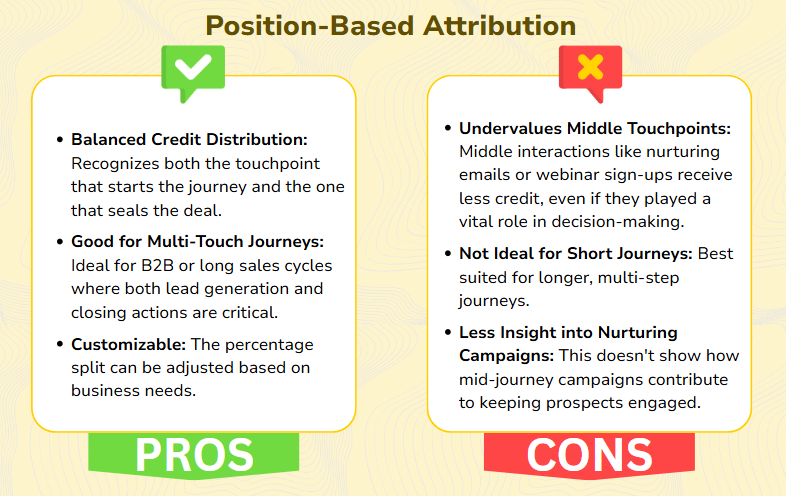
When to Use Position-Based Attribution:
This model works best when:
- You want to measure both lead generation and closing activities.
- Your campaigns have clear first and last interactions.
- You’re running multi-channel campaigns like paid ads, email, and content marketing.
6. Custom Attribution Models:
What are Custom Attribution Models?
Custom attribution models allow you to create your own rules for assigning credit to different touchpoints in a customer journey. Unlike standard models, custom models are tailored to match how customers interact with your brand, giving more accurate insights into what drives conversions.
With custom models, businesses can decide how much credit each touchpoint receives based on their unique sales process and customer behavior.
Examples of Custom Attribution Models:
- Weighted Model: Assigns higher credit to specific channels like email or paid ads if they are known to influence conversions more.
- Engagement-Based Model: Gives more credit to touchpoints where customers spend more time, like product demos or webinars.
- Multi-Channel Model: Splits credit differently based on whether the interaction happened on social media, email, or website.
Tools to Set Up Custom Attribution Models:
Several marketing platforms help businesses create and manage custom attribution models, including:
- Google Analytics (Custom Attribution Rules)
- Salesforce Marketing Cloud
- Adobe Marketo Measure
- HubSpot Attribution Reporting
- Oracle Eloqua Advanced Intelligence

When to Use Custom Attribution Models:
- For businesses with complex sales processes or multiple marketing channels.
- When standard attribution models don’t provide enough insights into customer behavior.
- If you need to measure the impact of specific campaigns or high-value touchpoints
- When combining offline and online touchpoints into one unified view.
Choosing the Right Attribution Model:
Key Takeaways: Agentforce in Salesforce
Choosing the right attribution model for your business is crucial to identifying which marketing activities contribute to conversions. However, there’s no one-size-fits-all model. The best choice depends on several factors unique to your business.
Key Factors to Consider:
- Sales Cycle Length:
Longer sales cycles with multiple touchpoints may benefit from Time-Decay or Position-Based (U-shaped) models, while shorter cycles might work better with First-Touch or Last-Touch models. - Business Goals:
If your goal is to generate brand awareness, First-Touch Attribution highlights early-stage efforts. For revenue-focused goals, models like Last-Touch or Time-Decay better emphasize closing interactions. - Customer Journey Complexity:
Businesses with multi-channel campaigns and multiple touchpoints may need Linear Attribution or Custom Models to get a holistic view.
Testing and Adapting Models Over Time:
No attribution model is perfect from the start. Regular testing and performance reviews are essential to:
- Identify gaps in the data.
- Adjust weight distribution across touchpoints.
- Adapt to changes in customer behavior or new marketing channels.
By continuously testing and refining your attribution model, you can gain more accurate insights and make data-driven decisions to optimize your marketing strategy.
Discover the Right Attribution Model for Your Business!
Subscribe to Newsletter
Get our latest blogs directly to your inbox.

